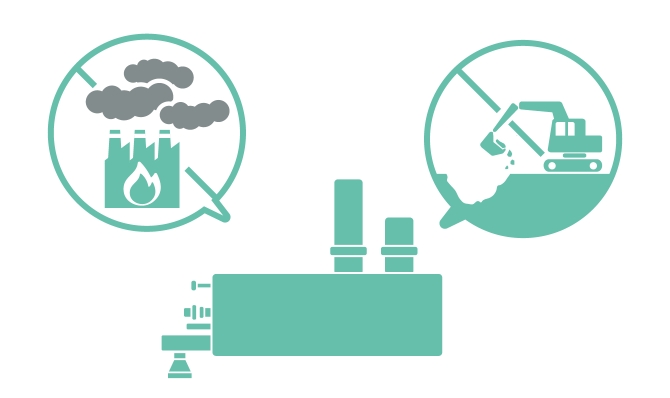
Subcritical Water Treatment Technology
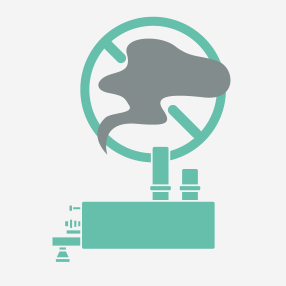
ALIN’s subcritical water treatment technology decomposes organic waste in a short time at an environment of 200 degrees Celsius and 20 MPa, making it odorless and harmless. This process allows for efficient waste treatment without generating greenhouse gasses, unlike the traditional incineration methods. Moreover, this technology is characterized by its ability to process various types of waste without segregating.
What is Subcritical Water?
Subcritical water refers to water that exists near the critical point, transitioning from a typical liquid state to a vaporized state under specific temperature and pressure conditions. Specifically, it is used under conditions of 200 degrees Celsius and 20 MPa.
Water in this subcritical state possesses stronger decomposition power than regular water, enabling efficient breakdown of organic matter.

Waste Treatment Process

Features of Subcritical Water Treatment


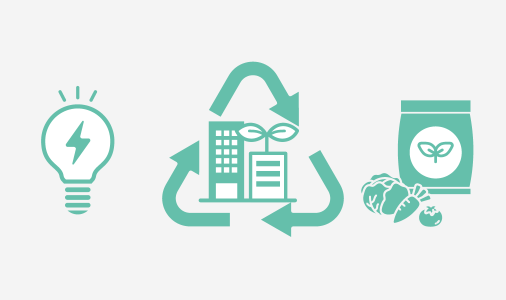
Reutilization of Waste and Building a Circular Society
Comparison with other treatment methods